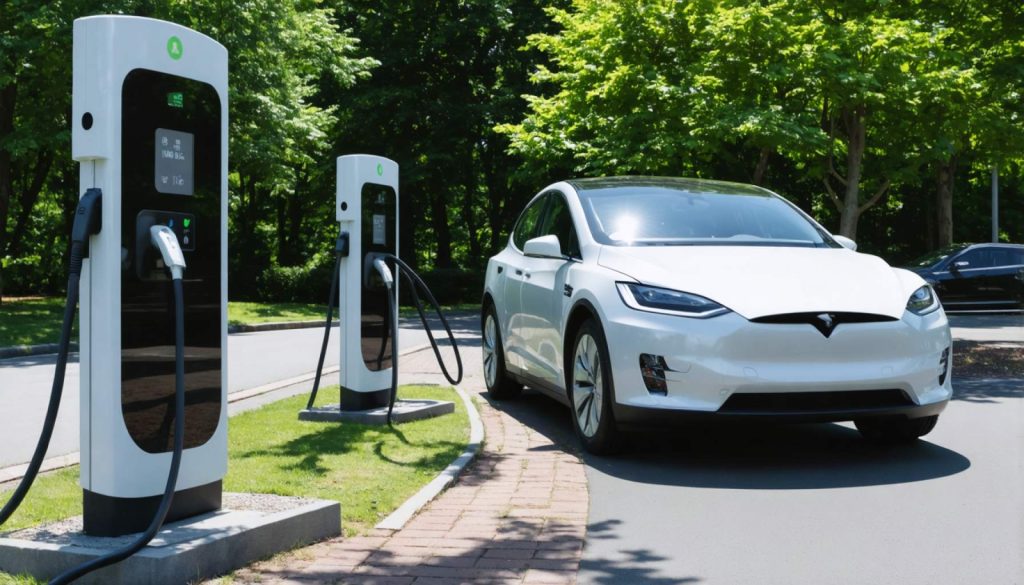
- Bidirectional electric vehicle (EV) chargers are revolutionizing energy consumption by enabling vehicles to both draw and return power, functioning like mobile power plants.
- The market for bidirectional chargers is set for substantial growth, expected to exceed $4.61 billion by 2031, driven by the push for zero-emission vehicles and global governmental support.
- Technological advancements, including faster charging speeds and enhanced load management, are key to realizing this vision.
- Challenges remain, such as the need for a unified global charging standard to align various regional regulations and infrastructures.
- Asia-Pacific is anticipated to lead adoption due to economic and environmental incentives, driven by fuel price rises and fossil fuel depletion.
- Collaborations, such as those between Fermata Energy and Phoenix Motorcars, highlight the collective effort to maximize bidirectional technology’s potential.
The hum of innovation grows louder with each passing day as the world transitions from fossil fuels to electrification. At the heart of this transformation are bidirectional electric vehicle (EV) chargers, a sophisticated technology set to redefine how we perceive energy consumption and transportation.
Imagine plugging your car in at night only to find that, by morning, it’s not just a vehicle, but a living part of a network. Bidirectional chargers create a dynamic dance of energy, enabling electric cars not just to draw power, but also to return it. This means they can essentially function as mobile power plants, connected to the grid and capable of distributing electricity when demand surges. It’s an electrifying vision of the future, where your vehicle contributes to your home’s power needs through Vehicle-to-Home (V2H) systems, or even sells energy back to the grid in a Vehicle-to-Grid (V2G) setup.
The market for these marvels is poised for explosive growth, projected to rocket past $4.61 billion by 2031, with a compound annual growth rate of 19.7%. This surge is powered by several factors, including the relentless drive for zero-emission vehicles, which have become symbols of a cleaner, greener tomorrow. Governments around the globe are bolstering this shift with fervent initiatives—carrot and stick measures designed to hasten the decline of gasoline addiction.
Underneath the hood, rapid technological advances paint a promising picture. Faster charging speeds, portable power stations, and enhanced load management turn this vision into reality. Innovations such as ultra-fast chargers and sophisticated automated payment systems are not only propelling the market forward but fundamentally altering the fabric of energy and transport sectors.
However, every hero has its challenges. For bidirectional chargers, it’s the race against the clock to create a unified charging standard that can be embraced worldwide, aligning the disparate and complex web of regional regulations and infrastructures.
Yet, the future shines brightly in places like Asia-Pacific, projected to be the fastest-growing adopter of these technologies. As nations face the harsh realities of fossil fuel depletion, soaring fuel prices have sparked a race to embrace cost-saving, sustainable alternatives. Here, electric vehicles serve not just as transportation but as gateways to a sustainable energy future.
Recently, collaborations between industry giants like Fermata Energy and Phoenix Motorcars have become the norm, pooling expertise to harness the full potential of bidirectional technology. Imagine a fleet of vehicles seamlessly integrating into city grids, smoothing out energy demand peaks and troughs like a well-rehearsed symphony.
The takeaway is clear: as we stand on the brink of this electric era, bidirectional chargers are not merely accessories for electric vehicles but pivotal players in a global energy ecosystem that promises efficiency, sustainability, and resilience. As this silent revolution gains momentum, it won’t just be the roadways reshaped—it will be energy as we know it.
How Bidirectional EV Chargers Are Rewiring Our Energy Future
Overview
Bidirectional electric vehicle (EV) chargers are poised to be game-changers in the transition from fossil fuels to electrification. Not only do they allow cars to draw power from the grid, but they also enable energy to be sent back from vehicles, allowing them to provide electricity to homes or even the grid itself. This is referred to as Vehicle-to-Home (V2H) and Vehicle-to-Grid (V2G) technology.
Unexplored Insights
1. How-To Steps & Life Hacks
– Installing a Bidirectional Charger at Home: Ensure compatibility with your EV model. Consult a professional for installation to align with local electrical codes. Consider your home’s energy capacity; your main electrical panel might need upgrades.
– Maximizing V2H and V2G Systems: Schedule charging during off-peak hours to take advantage of lower rates. Use energy management apps to optimize the energy flow and monitor savings.
2. Real-World Use Cases
– Emergency Power Supply: In case of a power outage, a fully charged EV with bidirectional capability can power essential home appliances for a limited period.
– Grid Support: Provide energy back to the grid during peak times, potentially reducing your electricity bill or earning credits.
3. Market Forecasts & Industry Trends
– Growth Potential: As reported, the bidirectional charger market is expected to exceed $4.61 billion by 2031. The development of smarter grid infrastructures and increased EV adoption will further fuel growth.
– Key Players: Companies such as Tesla, Nissan, and Fermata Energy are leading innovations in V2G and V2H technologies.
4. Controversies & Limitations
– Standardization Issues: A major barrier remains the lack of a universal charging standard. Different regions employ diverse protocols, creating potential compatibility issues.
– Battery Wear & Tear: Frequent use of V2G could lead to faster battery degradation, although manufacturers are continuously working to mitigate this.
5. Features, Specs & Pricing
– Charger Types: Home-use models tend to be slower but are sufficient for overnight charging, while commercial stations offer faster charges but require more infrastructure investment.
– Cost Considerations: Initial setup costs can be high due to the necessity of professional installation and potential home electrical upgrades.
6. Security & Sustainability
– Data Security: As chargers are connected to the home network, they are potentially vulnerable to cyber attacks. Regular software updates and using secure networks minimize risk.
– Environmental Impact: By facilitating the shift to EVs and renewable energy use, bidirectional chargers contribute significantly to reducing CO2 emissions.
7. Insights & Predictions
– Asia-Pacific Leadership: The Asia-Pacific region is expected to be a leader in adopting bidirectional technology due to higher electric vehicle adoption rates and governmental policies supporting renewable energy.
Actionable Recommendations
– For Homeowners: Evaluate your home’s electrical systems and potential cost savings before investing in a bidirectional charger.
– For Businesses: Consider integrating bidirectional charging into company parking areas to support sustainability goals and reduce operating costs.
– General Tips: Stay informed about local policies and incentives, as many governments offer rebates for installing renewable energy technologies.
Final Thoughts
Bidirectional chargers represent a pivotal shift towards sustainable energy use. As the technology advances and becomes more widely adopted, it will significantly reshape not only the transportation sector but also the broader energy landscape. Embracing this technology can lead to smarter energy consumption and production, providing resilience in an increasingly uncertain energy market.
Discover Nissan’s Sustainability Efforts